Algorithm
本周选择的算法题是:Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum。
规则
A path in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence at most once. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
The path sum of a path is the sum of the node’s values in the path.
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum path sum of any path.
Example 1:
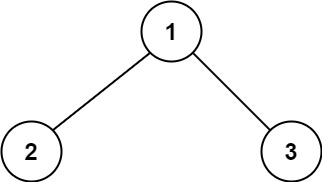
Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: 6
Explanation: The optimal path is 2 -> 1 -> 3 with a path sum of 2 + 1 + 3 = 6.
Example 2:
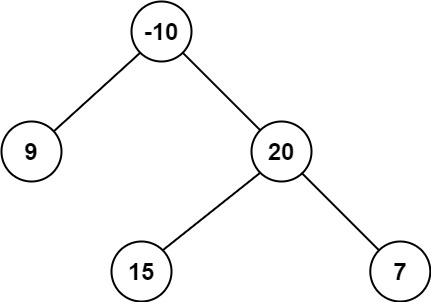
Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 42
Explanation: The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3 * 104]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solution
class Solution:
def maxPathSum(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
ans = float('-inf')
def _maxPathSum(node: TreeNode) -> int:
nonlocal ans
if not node: return 0
left_sum = max(_maxPathSum(node.left), 0)
right_sum = max(_maxPathSum(node.right), 0)
val = node.val + left_sum + right_sum
ans = max(ans, val)
return node.val + max(left_sum, right_sum)
_maxPathSum(root)
return ans
Review
Software Architecture - The Difference Between Architecture and Design
一篇想要描述「软件架构」与「软件设计」区别在哪的文章,文章主要谈论了:
- 软件架构 - 软件的高级抽象
- MicroServices
- Serverless
- Event-Driven
- …
- 软件设计 - 软件的代码细节
- SOLID
- …
- 常见的设计模式
我觉得这么区分不是特别好,架构设计是一门解决复杂问题的艺术,不同涉众看待架构的视角是不同的,因此架构师要为不同的涉众而设计,将复杂系统分而治之、以多个架构视图呈现的过程就是设计过程。
Tip
快手在业界开源了一款广受好评的 OOM 利器: KOOM,号称是内存问题杀手,刚好近期团队在关注可观测性这个方向,可以调研下。
