Algorithm
本周选择的算法题是:Clone Graph。
规则
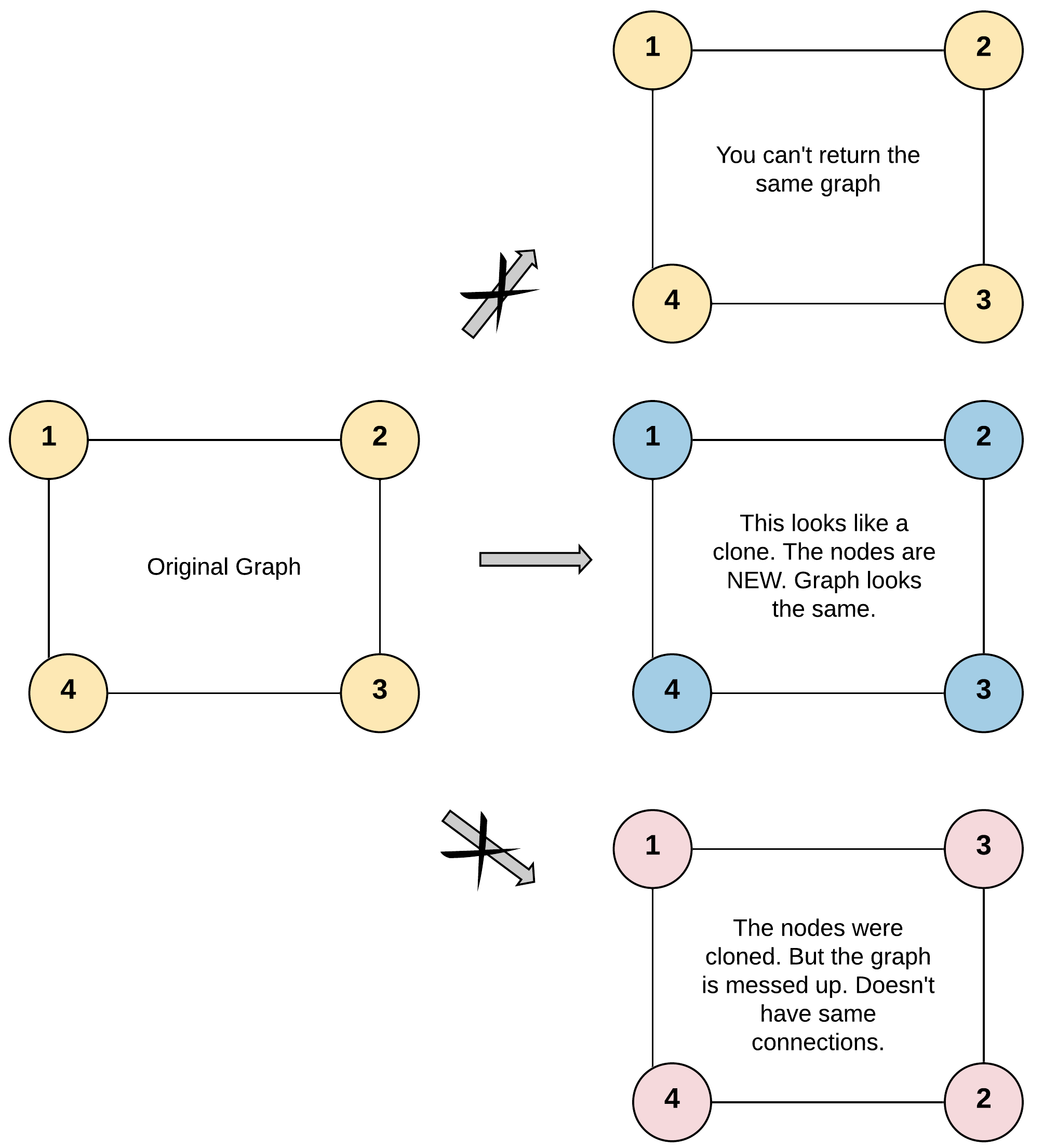
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a value (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
Test case format:
For simplicity, each node’s value is the same as the node’s index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val == 1, the second node with val == 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
An adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Example 1:
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph.
1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Example 2:
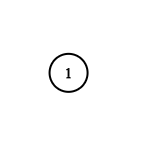
Input: adjList = [[]]
Output: [[]]
Explanation: Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.
Example 3:
Input: adjList = []
Output: []
Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the graph is in the range
[0, 100]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100Node.valis unique for each node.- There are no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
Solution
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val = 0, neighbors = None):
self.val = val
self.neighbors = neighbors if neighbors is not None else []
"""
class Solution:
def cloneGraph(self, node: 'Node') -> 'Node':
return self._clone(node, {})
def _clone(self, node: 'Node', map: dict) -> 'Node':
if not node: return node
if node.val in map: return map[node.val]
new_node = Node(node.val)
map[node.val] = new_node
for neighbor in node.neighbors:
new_node.neighbors.append(self._clone(neighbor, map))
return new_node
Review
Making the web better. With blocks!
Joel 最近搞了个 Block Protocol,希望能以 Block 为载体,使 web 真正做到能力共享。Block 本质是一段结构化的数据,是对功能集的封装,如果觉得概念不好理解,也能称为 components or widgets,但其抽象程度更高,因为它抹平了 React、Vue、Web Component 之间的差异,可以说 Block Protocol 一开始就是以建立 web 标准为目标的。
此外从 hash 源码和集成条件来看,BP 也是一个微应用规范,涵盖了渲染、数据验证、安全性、Machine-readable 等方面,该项目目前还处于起步阶段,公开的 Hub 只有 12 个 Blocks。
Tip
用 JS 检测 Dark Mode 的方法:
const prefersDarkMode = window.matchMedia("(prefers-color-scheme:dark)").matches; // true
