Algorithm
本周选择的算法题是:Add Two Numbers。
规则
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
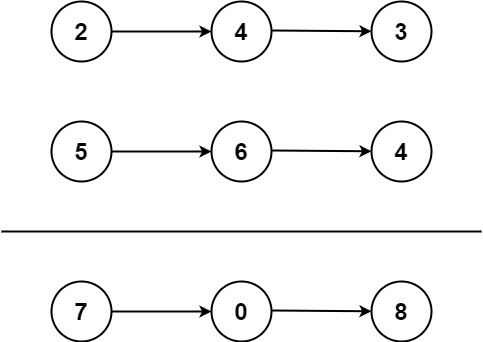
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
Output: [7,0,8]
Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
Example 2:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
Output: [0]
Example 3:
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
Solution
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
curr = dummy = ListNode()
carry = 0
while l1 or l2 or carry:
if l1:
carry += l1.val
l1 = l1.next
if l2:
carry += l2.val
l2 = l2.next
curr.next = ListNode(carry % 10)
carry = carry // 10
curr = curr.next
return dummy.next
Review
Anatomy of a perfect pull request
这篇文章用一张图表达了 CR 的痛点:
然后分享了如何把一个大 PR 拆解成 8 个小 PR:
- Create a model to save emails
- Create a route to receive requests
- Create a controller
- Create a service to save it in the database (business logic)
- Create a policy to handle access control
- Create a subscribe component (frontend)
- Create a button to call the subscribe component
- Add the subscribe button in the interface PR 也要符合单一原则 (Single Responsibility Principle),避免出现 Fat PR。
除了作者提到的方法,还有一些小技巧可以参考:
- 修复两个错误应该进行两次不同的提交
如果发现写提交信息时,需要写两点以上,则进行拆分提交
- 如果提交信息里含有“并且”、“而且”、“同时”等字眼时,也可以考虑拆分提交
从 git log 角度看,当查看某个文件的提交历史时,如果其提交信息的描述都是与此文件相关的,那就符合规范;如果发现某次的提交信息与本文件无关,则说明提交的时候误操作了。
Skinny PR 除了可以帮助开发团队明白其改动的用意,还能在出现问题时方便回滚,以及更安全的处理冲突。
Tip
在去年的#126里提到过,Django 将在 4.0 正式版提供官方的 Redis 支持,本周将公司内网的 Django 服务从 3.x 升至 4.x,学习并部署了 Redis,然后基于 Redis 实现了一个分布式锁的应用场景。
Share
过去自己弄错了一件事:没有很好理解绩效反馈的目的,在以坦承平等、释放潜力目标下,虽然我尽可能的提高了反馈的频率,以期望在第一时间给出改进建议,然而在过程中还是犯了关键性的错误,把绩效反馈当成了改善绩效,而不是提高绩效。
改善和提高两个词看似差异不大,但其实有本质区别:
- 改善 - 找到做得不够好的地方,期待下次做好
- 提高 - 找到改进空间,做到更好
忽视这个差异导致的直接后果是:在绩效反馈中,对于明星员工,只是努力地找出他们做得好的地方,并没有把心思放在如何提高他们的绩效上;而对于表现不佳的员工,则花了太多的精力告诉他们如何改进,希望通过明确的指示,让这些表现不佳的员工至少达到岗位要求的最低标准。
更好的做法应该反过来,在明星员工身上多花些时间,因为公司的成功很大部分是取决于这部分人,而且努力提高他们的绩效会得到更高的杠杆率,如果他们能做得更好,对整个组织产生的影响无疑会更大。
无论一个明星员工表现得多好,他总还是会有改进的余地,虽然批评人很难,特别是面对一个明日巨星时,但如果因此采用看似得体的方式减小反馈的难度,也会让他错过不断进步的机会,从而违背了反馈的初衷 – 绩效反馈要以提高绩效为目标。
