Algorithm
本周选择的算法题是:Design Underground System。
规则
An underground railway system is keeping track of customer travel times between different stations. They are using this data to calculate the average time it takes to travel from one station to another.
Implement the UndergroundSystem class:
void checkIn(int id, string stationName, int t)- A customer with a card ID equal to
id, checks in at the stationstationNameat timet. - A customer can only be checked into one place at a time.
- A customer with a card ID equal to
void checkOut(int id, string stationName, int t)- A customer with a card ID equal to
id, checks out from the stationstationNameat timet.
- A customer with a card ID equal to
double getAverageTime(string startStation, string endStation)- Returns the average time it takes to travel from
startStationtoendStation. - The average time is computed from all the previous traveling times from
startStationtoendStationthat happened directly, meaning a check in atstartStationfollowed by a check out fromendStation. - The time it takes to travel from
startStationtoendStationmay be different from the time it takes to travel fromendStationtostartStation. - There will be at least one customer that has traveled from
startStationtoendStationbeforegetAverageTimeis called.
- Returns the average time it takes to travel from
You may assume all calls to the checkIn and checkOut methods are consistent. If a customer checks in at time t1 then checks out at time t2, then t1 < t2. All events happen in chronological order.
Example 1:
Input
["UndergroundSystem","checkIn","checkIn","checkIn","checkOut","checkOut","checkOut","getAverageTime","getAverageTime","checkIn","getAverageTime","checkOut","getAverageTime"]
[[],[45,"Leyton",3],[32,"Paradise",8],[27,"Leyton",10],[45,"Waterloo",15],[27,"Waterloo",20],[32,"Cambridge",22],["Paradise","Cambridge"],["Leyton","Waterloo"],[10,"Leyton",24],["Leyton","Waterloo"],[10,"Waterloo",38],["Leyton","Waterloo"]]
Output
[null,null,null,null,null,null,null,14.00000,11.00000,null,11.00000,null,12.00000]
Explanation
UndergroundSystem undergroundSystem = new UndergroundSystem();
undergroundSystem.checkIn(45, "Leyton", 3);
undergroundSystem.checkIn(32, "Paradise", 8);
undergroundSystem.checkIn(27, "Leyton", 10);
undergroundSystem.checkOut(45, "Waterloo", 15); // Customer 45 "Leyton" -> "Waterloo" in 15-3 = 12
undergroundSystem.checkOut(27, "Waterloo", 20); // Customer 27 "Leyton" -> "Waterloo" in 20-10 = 10
undergroundSystem.checkOut(32, "Cambridge", 22); // Customer 32 "Paradise" -> "Cambridge" in 22-8 = 14
undergroundSystem.getAverageTime("Paradise", "Cambridge"); // return 14.00000. One trip "Paradise" -> "Cambridge", (14) / 1 = 14
undergroundSystem.getAverageTime("Leyton", "Waterloo"); // return 11.00000. Two trips "Leyton" -> "Waterloo", (10 + 12) / 2 = 11
undergroundSystem.checkIn(10, "Leyton", 24);
undergroundSystem.getAverageTime("Leyton", "Waterloo"); // return 11.00000
undergroundSystem.checkOut(10, "Waterloo", 38); // Customer 10 "Leyton" -> "Waterloo" in 38-24 = 14
undergroundSystem.getAverageTime("Leyton", "Waterloo"); // return 12.00000. Three trips "Leyton" -> "Waterloo", (10 + 12 + 14) / 3 = 12
Example 2:
Input
["UndergroundSystem","checkIn","checkOut","getAverageTime","checkIn","checkOut","getAverageTime","checkIn","checkOut","getAverageTime"]
[[],[10,"Leyton",3],[10,"Paradise",8],["Leyton","Paradise"],[5,"Leyton",10],[5,"Paradise",16],["Leyton","Paradise"],[2,"Leyton",21],[2,"Paradise",30],["Leyton","Paradise"]]
Output
[null,null,null,5.00000,null,null,5.50000,null,null,6.66667]
Explanation
UndergroundSystem undergroundSystem = new UndergroundSystem();
undergroundSystem.checkIn(10, "Leyton", 3);
undergroundSystem.checkOut(10, "Paradise", 8); // Customer 10 "Leyton" -> "Paradise" in 8-3 = 5
undergroundSystem.getAverageTime("Leyton", "Paradise"); // return 5.00000, (5) / 1 = 5
undergroundSystem.checkIn(5, "Leyton", 10);
undergroundSystem.checkOut(5, "Paradise", 16); // Customer 5 "Leyton" -> "Paradise" in 16-10 = 6
undergroundSystem.getAverageTime("Leyton", "Paradise"); // return 5.50000, (5 + 6) / 2 = 5.5
undergroundSystem.checkIn(2, "Leyton", 21);
undergroundSystem.checkOut(2, "Paradise", 30); // Customer 2 "Leyton" -> "Paradise" in 30-21 = 9
undergroundSystem.getAverageTime("Leyton", "Paradise"); // return 6.66667, (5 + 6 + 9) / 3 = 6.66667
Constraints:
1 <= id, t <= 1061 <= stationName.length, startStation.length, endStation.length <= 10- All strings consist of uppercase and lowercase English letters and digits.
- There will be at most
2 * 104calls in total tocheckIn,checkOut, andgetAverageTime. - Answers within
10-5of the actual value will be accepted.
Solution
class UndergroundSystem:
def __init__(self):
self.checkIns = dict()
self.routeTimes = defaultdict(int)
self.routeCount = defaultdict(int)
def checkIn(self, id: int, stationName: str, t: int) -> None:
self.checkIns[id] = stationName, t
def checkOut(self, id: int, stationName: str, t: int) -> None:
startStation, startTime = self.checkIns.pop(id)
routeName = startStation, stationName
self.routeTimes[routeName] += t - startTime
self.routeCount[routeName] += 1
def getAverageTime(self, startStation: str, endStation: str) -> float:
routeName = startStation, endStation
return self.routeTimes[routeName] / self.routeCount[routeName]
# Your UndergroundSystem object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = UndergroundSystem()
# obj.checkIn(id,stationName,t)
# obj.checkOut(id,stationName,t)
# param_3 = obj.getAverageTime(startStation,endStation)
Review
Ajax Battle: XMLHttpRequest vs the Fetch API
Fetch 的优势:
XMLHttpRequest 的优势:
- 可以通过
onprogress实现进度追踪 - 支持超时设置
- 不像 Fetch 的 AbortController,可以轻易实现中断
- 对低版本浏览器(IE 或 2015 年以前的浏览器版本)的兼容性更好
Tip
一款基于 Rust 的高性能终端应用:Warp,主要特点如下:
- 高性能 - Rust + Metal,纯 native 应用,由于 MacOS 是第一目标平台,选择了 Metal over OpenGL 作为 GPU API
- 实时协同 - 基于 Rust 开发了 SumTree + CRDT 数据结构的编辑器,支持编辑器内实时协同,支持通过链接共享输出
- 更好的开发体验 - 像写代码一样操作终端,块选择、块编辑、自动完成、workflow 都是基本功能
- 值得注意的是,他们会对用户数据进行分析 - 基于 telemetry
作为一款新产品,难免有 bug:
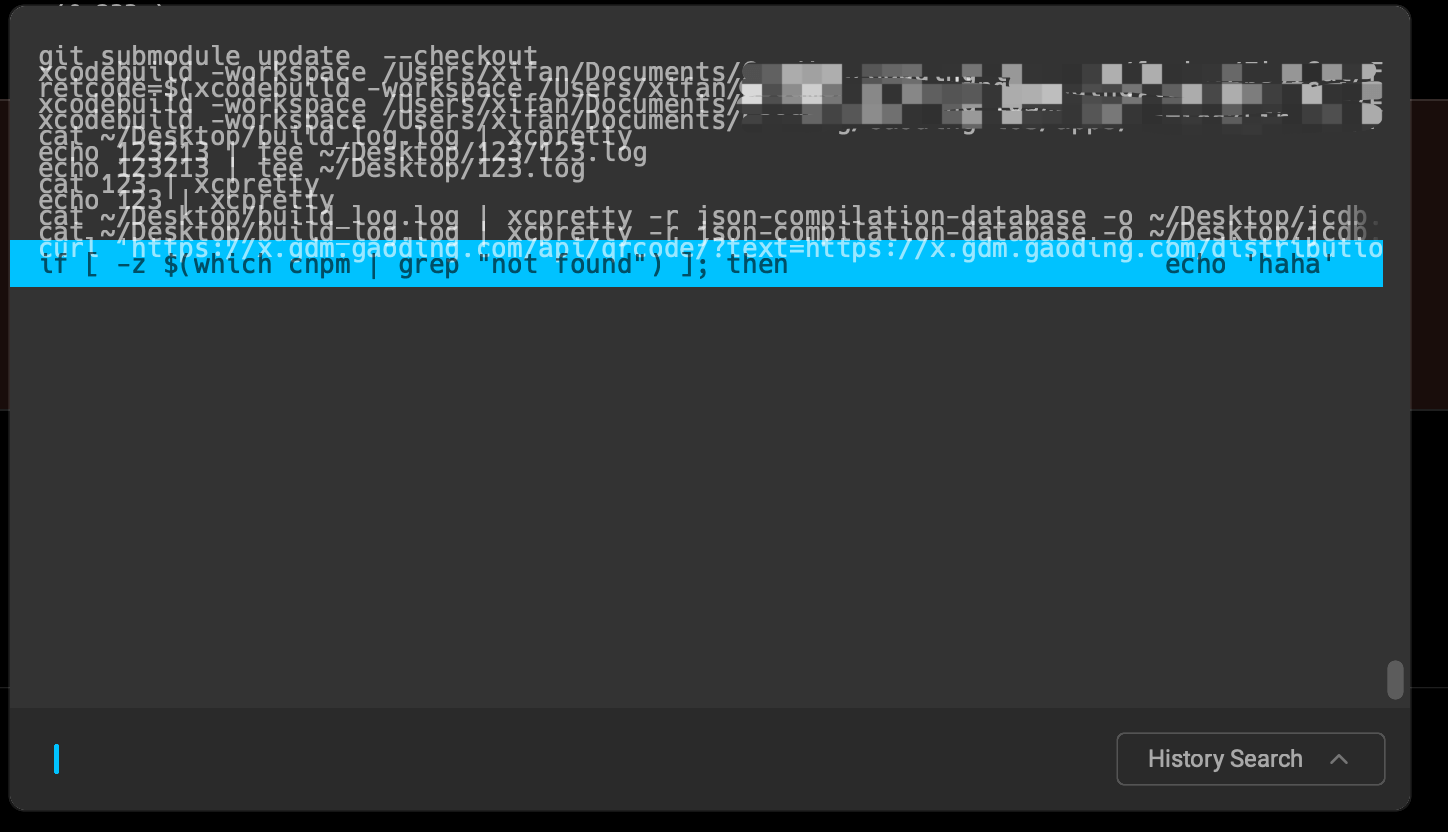
再继续使用看看~
Share
2022 上半年快过完了,过去这四个月最大感受是好像做了很多事,又好像啥也没干,看书的进度倒是超出了自己预期,干脆记录下读完也许你该找个人聊聊的六个感受吧:
- 完美是幸福的敌人
- 不用期望别人来告诉自己该干什么,就好像别人手里有标准答案似的,又好像我们每天在日常生活中做的那么多选择真的有对错之分
- 变化往往伴随着失去。如果总说改变,却依然驻足原地,恐怕是不知道变化会令人失去什么,而且大多数巨变都是靠我们用数百个微不足道、甚至难以察觉的一小步累积而来的,一步之中蕴含着许多可能性
- 安宁,不是要身处一个没有嘈杂、烦恼和辛劳的地方,而是即使身处于繁杂之中依然保持内心的平静
- 不言而喻的讽刺:人们想给自己的问题找到一个快速的解决方案,但殊不知一开始导致他们情绪问题的,就是生活中太过匆忙的节奏。他们以为现在的忙碌是为了以后能有机会享受生活,但往往,后来就没有“后来”了
五一期间打算看完跟老婆一起带孩子。
