Algorithm
本周选择的算法题是:Container With Most Water
规则如下:
Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, …, an , where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of line i is at (i, ai) and (i, 0). Find two lines, which together with x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Note: You may not slant the container and n is at least 2.
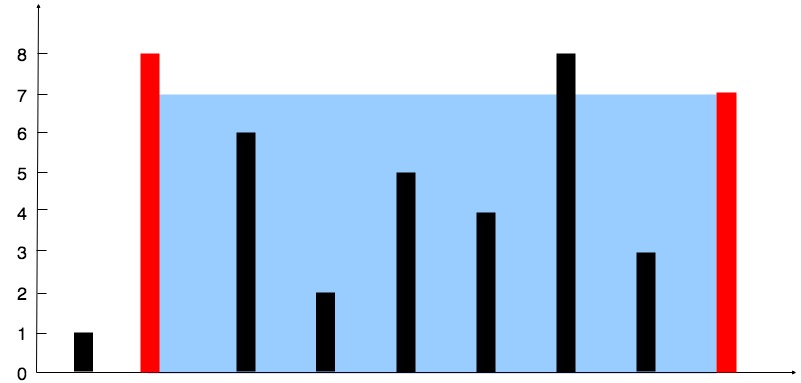
The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example:
Input: [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
Solution
我实现的方案:
Runtime:140 ms,快过 83.13%。
Memory:15.2 MB,低于 5.26%。
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
left, right = 0, len(height) - 1
water = 0
while left < right:
minimum = min(height[left], height[right])
water = max(minimum * (right - left), water)
while height[left] <= minimum and left < right:
left += 1
while height[right] <= minimum and left < right:
right -= 1
return water
这是优化后的实现,最初的实现是没有记录 minimum,导致后续的值如果继续比 minimum 小的话会有时间上的浪费。
Review
这篇文章相当于把 Calling convention 重新讲了一遍。问题的引子是 objc_msgSend 的原型发生了变化:
由
id objc_msgSend(id self, SEL _cmd, ...)
变成了:
void objc_msgSend(void)
可以看出旧的原型可以直接使用:
objc_msgSend(obj, selector, param1);
但是实现上没办法通过 C 来实现。
这就是上面提到的 Calling convention,不同的 ABI 对参数传递的要求是不同的,比如 Intel ABI 的整型参数是存储在 rdi, rsi,rdx, rcx,r8, r9 这几个寄存器里,ARM64 ABI 则是存储在 x0...x7 里,对于变长参数 variadic,Intel ABI 需要在 %al(%rax 的低位) 里记录使用 SSE 寄存器的数量,而 ARM64 ABI 则总是通过栈来传递 variadic。
因为 objc_msgSend 是一个通用接口,它只在调用时才知道参数、返回值的类型,系统层面已经不能帮它在寄存器里传递参数,它的实现实际是根据不同的 ABI 写不同的汇编代码。
回到原型变化的问题。
C 语言在处理 variadic 时,可能会有类型提升:
- char、short => int
- float => double
对于整型来说还好,字节上是对齐的,很容易填充,但是对于 float 来说则是灾难,它将产生完全不同的值:
// Use the old variadic prototype for objc_msgSend.
#define OBJC_OLD_DISPATCH_PROTOTYPES 1
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import <objc/message.h>
@interface Foo : NSObject @end
@implementation Foo
- (void)log: (float)x {
printf("%f\n", x);
}
@end
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
id obj = [Foo new];
[obj log: (float)M_PI];
objc_msgSend(obj, @selector(log:), (float)M_PI);
}
// 3.141593
// 3370280550400.000000
这类问题从 Runtime 第一个版本开始就存在了,一旦碰见很难排查。对此苹果希望我们使用新的原型:
void objc_msgSend(void);
相比旧的原型,它不能直接使用,你需要显式将它转成你期望的形式,然后调用它。
Tip
/dev/null 是一个软件实现的虚拟硬件设备:
- 从它读取到的值是“空”的
- 写给它的值会“消失”
最常见的用法是让命令以静默的方式执行(stdout 被写给了 null):
command > /dev/null
它还有一种常见的用法是创建一个空文件,如果这个文件原本就存在,则清空它的内容:
cat /dev/null > file
关于重定向的用法总结:
file可以是一个 device node- 如果文件不存在,它会创建一个标准的文件
- 如果文件存在而且不为空,它会被覆盖
- 如果文件存在且是一个 symbolic link,则会使用指向的原始文件
- 如查文件存在且是一个目录,则会报错:
bash: *file*: Is a directory
更多解释参见: What does /dev/null mean in a shell script?
Share
本周写了几个用于自动化部署的脚本,支持用 which、pip3 和 gem 来判断对应版本的依赖有没有安装,如果没有安装则直接略过,可以减少执行的时间。这三种方式几乎可以涵盖所有的依赖的检测:
# which
if [ -z $(which python3) ]; then
brew install python3
else
echo "python3 is installed"
fi
# pip3
result=$(pip3 show bs4)
if [ -z "$result" ]; then
pip3 install bs4
else
echo "bs4 is installed"
fi
# gem
install_if_not_installed() {
if gem list -i $1 -v $2 > /dev/null; then
echo "$1 is installed"
else
gem install $1 -v $2
fi
}
install_if_not_installed cocoapods 1.8.0
install_if_not_installed xcpretty 0.3.0
install_if_not_installed slather 2.4.7
