Algorithm
本周选择的算法题是:Unique Paths
规则如下:
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked ‘Start’ in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked ‘Finish’ in the diagram below).
How many possible unique paths are there?
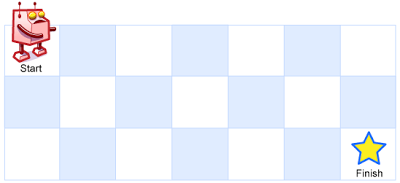 Above is a 7 x 3 grid. How many possible unique paths are there?
Above is a 7 x 3 grid. How many possible unique paths are there?
Example 1:
Input: m = 3, n = 2
Output: 3
Explanation:
From the top-left corner, there are a total of 3 ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1. Right -> Right -> Down
2. Right -> Down -> Right
3. Down -> Right -> Right
Example 2:
Input: m = 7, n = 3
Output: 28
Constraints:
1 <= m, n <= 100- It’s guaranteed that the answer will be less than or equal to
2 * 10 ^ 9.
Solution
我实现的方案:
Runtime:24 ms,快过 89.59%。
Memory:12.7 MB,低于 100%。
class Solution:
def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int:
current = [1] * n
for _ in range(1, m):
for j in range(1, n):
current[j] += current[j-1]
return current[-1]
这道题挺有趣的,从最初解法到最终解法我经历了以下几个步骤。
首先,用 dp 实现的最初版本:
class Solution:
def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int:
if m == 0 or n == 0: return 0
if m == 1 and n == 1: return 1
return self.uniquePaths(m - 1, n) + self.uniquePaths(m, n - 1)
由于存在大量的重复路径,这个解法是超时的。
之后是加上缓存的版本:
class Solution:
def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int:
dp = [[1] * n for i in range(m)]
for i in range(1, m):
for j in range(1, n):
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1]
return dp[m-1][n-1]
缓存很有用,不过由于只用到了当前行 dp[i] 和前一行dp[i-1],所以内存上有改善空间。
class Solution:
def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int:
previous, current = [1] * n, [1] * n
for _ in range(1, m):
for j in range(1, n):
current[j] = previous[j] + current[j-1]
previous, current = current, previous
return previous[-1]
内存也得到了进一步的改善,但是观察之后很容易发现 previous[j] 的取值就是当前值,此处再优化后便是最终版本。
Review
How Operating Systems Work: 10 Concepts you Should Know as a Developer
作为一名软件工程师,需要关注整个计算机行业的发展,包括但不限于硬件、操作系统、网络、数据管理和挖掘等领域,了解越多就越容易与其他领域的人交流。
操作系统的工作原理属于基础技术,基础技术又是各种上层技术的基石,吃透基础技术才有助于提高学习能力。
Tip
先看一段简单的 python 代码:
def extendList(val, list=[]):
list.append(val)
return list
list1 = extendList(10)
list2 = extendList(123,[])
list3 = extendList('a')
print "list1 = %s" % list1
print "list2 = %s" % list2
print "list3 = %s" % list3
输出结果是什么呢?在看下面的答案之前可以先自己想一想:
list1 = [10, 'a'] --> ???
list2 = [123]
list3 = [10, 'a'] --> ???
出现这个结果是因为表达式的计算发生在方法定义时,而不是方法调用时。
list1 和 list3 使用了同一个列表,所以它们的取值是一样的。
Share
读《如何成为一个大家愿意追随的 Leader?》有感。
Leader 除了技术领导力之外,还需要:
- 赢得他人的信任 - 别人愿意向你打开心扉,和你说他心里最柔软的东西,这才是真正的信任
- 开放的心态 + 倾向性的价值观 - 对新生事物要有开放的心态,对每个人的观点要有开放的心态,但并不是要认同所有的观点和事情
- Lead By Example - 以身作则,展示怎么做,以及 Always Be Coding,要能非常明白一个技术方案的优缺点,实现复杂度,知道什么是最佳实践,你的方案才会更具执行力和实践性。
- 保持热情和冲劲 - 正视问题,正视不足,正视错误,从中进行反思和总结得到更好的解决方案
- 能够抓住重点,看透事物的本质 - 作为一个 Leader,能够抓住主要矛盾,看清事物的本质,给出清楚的观点或方向,简化复杂的事情。
- 描绘令人激动的方向,提供令人向往的环境 - 一个好的 Leander 一定会把每人人心中最真善美的东西呼唤出来,并且还能让人相信这是有机会有可能做到的。
- 甘当铺路石,为他人制造机会 - Leader 不从团队收割成绩,而是给予团队成绩,成就他人其实也是在成就自己。
