Algorithm
本周选择的算法题是:Vowel Spellchecker
规则如下:
Given a wordlist, we want to implement a spellchecker that converts a query word into a correct word.
For a given query word, the spell checker handles two categories of spelling mistakes:
- Capitalization: If the query matches a word in the wordlist (case-insensitive), then the query word is returned with the same case as the case in the wordlist.
- Example:
wordlist = ["yellow"],query = "YellOw":correct = "yellow" - Example:
wordlist = ["Yellow"],query = "yellow":correct = "Yellow" - Example:
wordlist = ["yellow"],query = "yellow":correct = "yellow"
- Example:
- Vowel Errors: If after replacing the vowels (‘a’, ‘e’, ‘i’, ‘o’, ‘u’) of the query word with any vowel individually, it matches a word in the wordlist (case-insensitive), then the query word is returned with the same case as the match in the wordlist.
- Example:
wordlist = ["YellOw"],query = "yollow":correct = "YellOw" - Example:
wordlist = ["YellOw"],query = "yeellow":correct = ""(no match) - Example:
wordlist = ["YellOw"],query = "yllw":correct = ""(no match)
- Example:
In addition, the spell checker operates under the following precedence rules:
- When the query exactly matches a word in the wordlist (case-sensitive), you should return the same word back.
- When the query matches a word up to capitlization, you should return the first such match in the wordlist.
- When the query matches a word up to vowel errors, you should return the first such match in the wordlist.
- If the query has no matches in the wordlist, you should return the empty string.
Given some queries, return a list of words answer, where answer[i] is the correct word for query = queries[i].
Example 1:
Input: wordlist = ["KiTe","kite","hare","Hare"], queries = ["kite","Kite","KiTe","Hare","HARE","Hear","hear","keti","keet","keto"]
Output: ["kite","KiTe","KiTe","Hare","hare","","","KiTe","","KiTe"]
Note:
1 <= wordlist.length <= 50001 <= queries.length <= 50001 <= wordlist[i].length <= 71 <= queries[i].length <= 7- All strings in
wordlistandqueriesconsist only of english letters.
Solution
我实现的方案:
Runtime:128 ms,快过 96.77%。
Memory:14,8 MB,低于 100%。
class Solution:
vowel_table = set(['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'])
def spellchecker(self, wordlist: List[str], queries: List[str]) -> List[str]:
if len(queries) == 0:
return []
def replace_vowel(word: str) -> str:
return "".join([char if char not in Solution.vowel_table else "a" for char in word])
hash_table = set(wordlist)
word_lower_table = {}
word_vowel_table = {}
for word in wordlist:
word_lower = word.lower()
word_lower_table.setdefault(word_lower, word)
word_vowel_table.setdefault(replace_vowel(word_lower), word)
result = [""] * len(queries)
i = 0
for query in queries:
# exactly matches a word
if query in hash_table:
result[i] = query
else:
query_lower = query.lower()
# matches a word up to capitlization
if query_lower in word_lower_table:
result[i] = word_lower_table[query_lower]
else:
query_without_vowel = replace_vowel(query_lower)
# matches a word up to vowel errors
if query_without_vowel in word_vowel_table:
result[i] = word_vowel_table[query_without_vowel]
i += 1
return result
规则有点多,特别是元音匹配这里卡了很久,最终还是决定用一张表来处理。这道题也有官方解法,经过对比发现实现思路是一样的,不过具体的实现没有官方优雅,result 的构造过程直接用一个 map 就可以了,可以有效避免多层 if 嵌套。这说明我的函数式编程思维还需要锻炼。
Review
Understanding Asynchronous JavaScript
该文用非常简洁、通畅的语句解释了 JavaScript 是如何实际异步回调的。在此总结下:
The Event Loop
JavaScript 本身是单线程的,不支持异步/多线程,为此需要浏览器或解释环境提供支持。如下图所示: 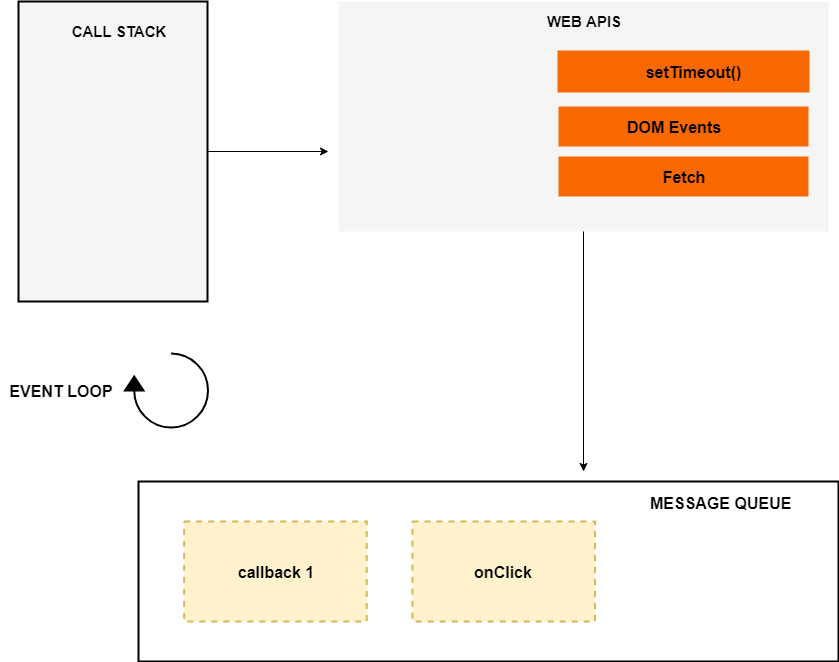 图中的 event loop、web APIs 和 message queue(或叫 task queue)并不属于 JavaScript 引擎,这是浏览器或其他 JavaScript 运行环境提供的能力。call stack 只有一个,因为是单线程;web APIs 提供了一些方法来做异步回调,它会在需要时将回调给到 message queue,然后 event loop 会检查 call stack 是不是空的,如果是空的,且 message queue 中有回调,则会把 message queue 中的回调 pop,然后 push 到 call stack 中来执行。
图中的 event loop、web APIs 和 message queue(或叫 task queue)并不属于 JavaScript 引擎,这是浏览器或其他 JavaScript 运行环境提供的能力。call stack 只有一个,因为是单线程;web APIs 提供了一些方法来做异步回调,它会在需要时将回调给到 message queue,然后 event loop 会检查 call stack 是不是空的,如果是空的,且 message queue 中有回调,则会把 message queue 中的回调 pop,然后 push 到 call stack 中来执行。
DOM Events
DOM Events的处理过程也类似,web APIs 环境会在事件触发时 push 给 message queue,之后由 event loop 来处理。整个过程看起来如下: 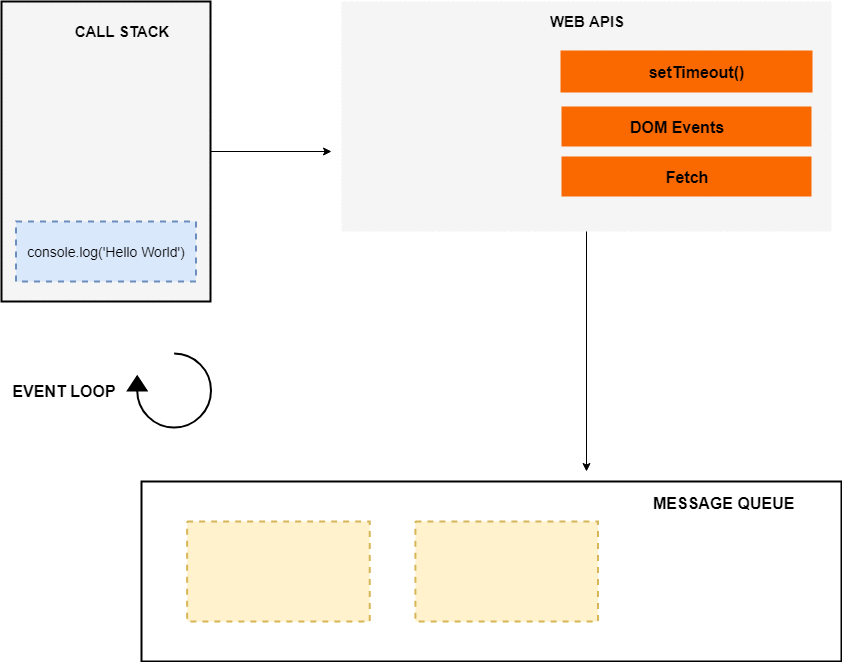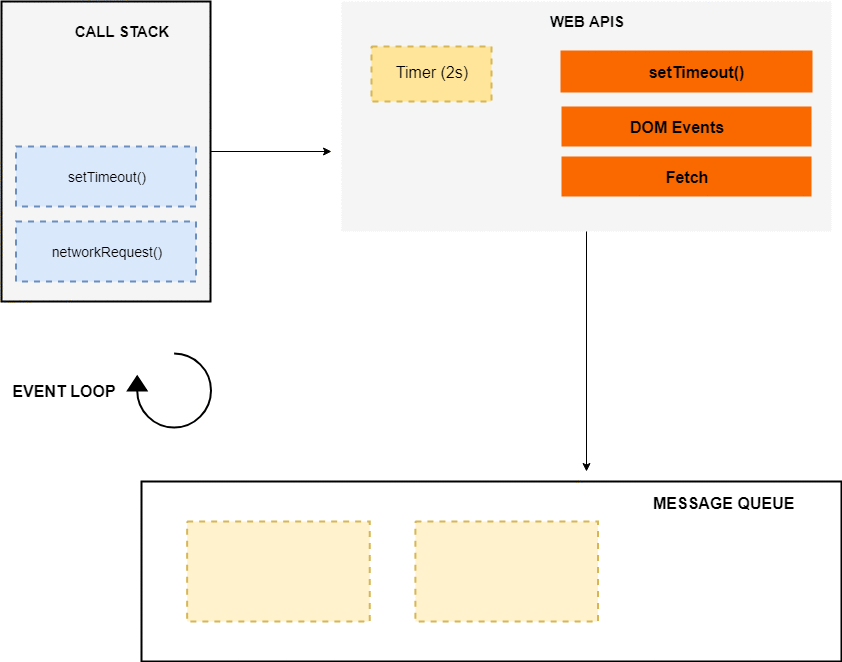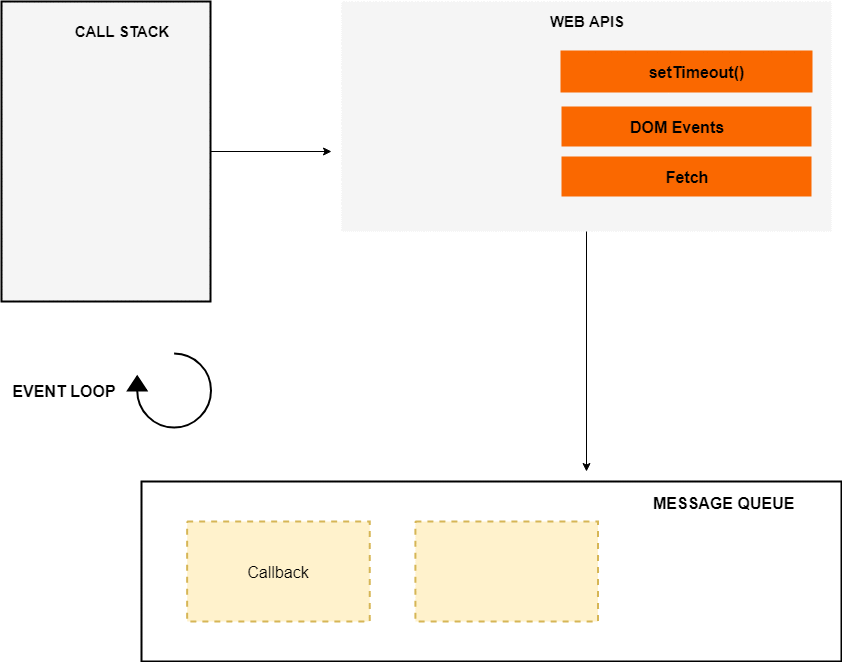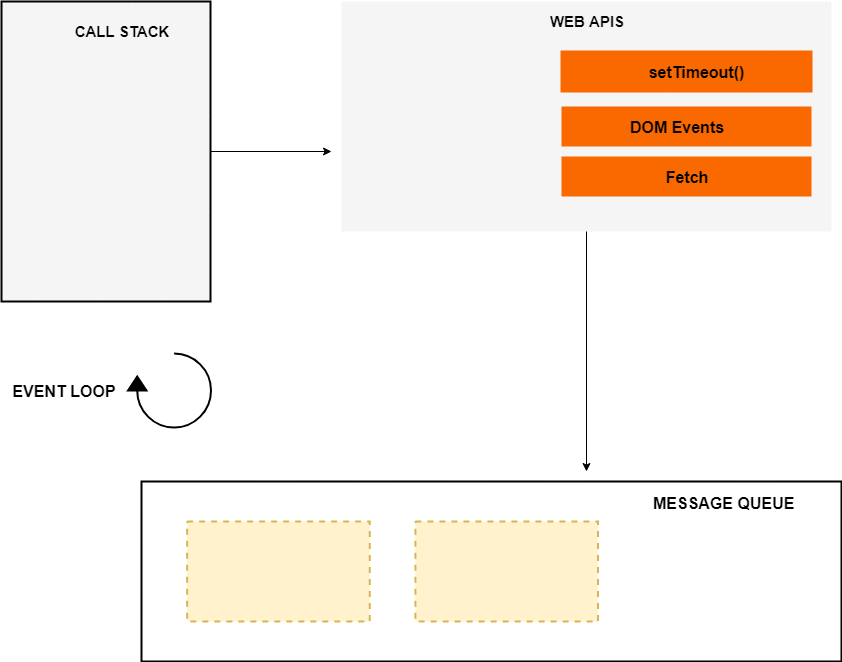
ES6 Job Queue/Micro-Task Queue
ES6 引入了 Job Queue(又称 Micro-Task Queue),它与 message queue 的概念很像,不同的是 job queue 的优先总是高于 message queue,也就是说,除非 job queue 是空的,不然 message queue 中的回调不会被执行。
例子一
console.log('Script start');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout');
}, 0);
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('Promise resolved');
}).then(res => console.log(res))
.catch(err => console.log(err));
console.log('Script End');
输出是:
Script start
Script End
Promise resolved
setTimeout
例子二
console.log('Script start');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout 1');
}, 0);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout 2');
}, 0);
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('Promise 1 resolved');
}).then(res => console.log(res))
.catch(err => console.log(err));
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('Promise 2 resolved');
}).then(res => console.log(res))
.catch(err => console.log(err));
console.log('Script End');
输出是:
Script start
Script End
Promise 1 resolved
Promise 2 resolved
setTimeout 1
setTimeout 2
例子三
console.log('Script start');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout');
}, 0);
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('Promise 1 resolved');
}).then(res => console.log(res));
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('Promise 2 resolved');
}).then(res => {
console.log(res);
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('Promise 3 resolved');
})
}).then(res => console.log(res));
console.log('Script End');
输出是:
Script start
Script End
Promise 1 resolved
Promise 2 resolved
Promise 3 resolved
setTimeout
这些例子展示了 job queue 与 message queue 之间的优先级。
Tip
本周学习到的一些内容:
- 完成了从 PyCharm 到 VS Code 的过渡
- Python 爬虫的一些实战经验
- 在 Python 中可以这样将元组映射到方法参数中:
func(*tuple) - JavaScript 的异步处理机制
Share
几年后,我打算重新在公共平台记录自己的成长:
- 公共平台的写作能锻炼自己的沟通能力
- 公共平台的写作能通过给自己压力,将零散的知识点形成系统性的认识
- 知识不是死记硬背,持续获取知识的能力更重要
- 学习需要持续,而成长却看起来不是“持续”的,它不会对学习产生即时反馈,它可能会有某个点突然出现,然后一夜长大,在它长大之前,耐心培育它吧
为此我在7月3号购买了 CodingTour 这个域名,用于记录自己的所看、所思、所想。
Learning to be better。
在分享一篇我选择域名时看到的文章吧
How to Choose the Best Domain Name(11 Tips and Tools)
一个有追求有品位的程序员应该要有自己独立域名的个人主页吧,这会给人一种爱动手做事的感觉。 在此对该文做个记录,方便索引。
选择好域名的14个提示:
- 坚持
.com域名- 更可信
- 更容易记住,大多数人输入网址的时候会下意识输入
.com - 一些机器(比如智能手机)也只提供了
.com的按钮让人快速输入
- 在域名中使用关键字
- 关键字能更容易让搜索引擎索引,也更容易取得排名靠前的位置
- 保持域名的简短
- 太长的域名不好记
- 太长的域名更容易拼写错误
- 建议域名不要超过15个字符
- 容易拼写和容易读
- 唯一性和可品牌化
- 不要使用别人的商标名或已有的同名服务
- 唯一性是为了和其他人的服务区分开,不让你的流量流向别的地方
- 品牌更容易传播和好记,Amazom.com 就比 BuyBooksOnline.com 更好
- 不要使用
-- 怪异的符号通常会和垃圾域名联想在一起
- 容易写错域名
- 不要使用重复字母
- 重复的域名同样不好记,也更容易出现拼写错误,比如 Processsetup.com
- 留有扩充的余地
- 选择更抽象、不依赖当前业务的名称,这样当你的业务拓展到其他领域的时候,不用切换到新的域名从而导致损失
- 调查下你的域名
- 注册域名前先在索引擎或社交媒体上搜索下你的域名,和商标相似的名称可能会给你带来法律风险,从而导致经济上的损失
- 使用域名生成器得到一些灵感
- 大多数好的域名已经被人占用,域名生成器将会通过组合关键字生成一些好记、又短的域名,帮助你做出选择
- 比其他人先得到它
- 每天都有大量的域名被注册,你如果找到了一个你觉得还不错的域名,应该尽快完成注册
- 注册域名的最佳地方
- 获取免费的域名和托管服务器
- 最受欢迎的域名注册商
12 到 14 这三个 Tips 属于文章标题中的 Tools,借鉴意义没有那么大。国内用户直接使用腾讯或者阿里的服务就好。
