Algorithm
本周选择的算法题是:Minimum Path Sum。
规则
Given a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right, which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.
Note: You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Example 1:
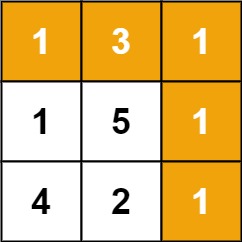
Input: grid = [[1,3,1],[1,5,1],[4,2,1]]
Output: 7
Explanation: Because the path 1 → 3 → 1 → 1 → 1 minimizes the sum.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]
Output: 12
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= grid[i][j] <= 100
Solution
标准的 DP 解法:
class Solution:
def minPathSum(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
dp = [[float('inf')] * (n+1) for _ in range(m+1)]
dp[0][1], dp[1][0] = 0, 0
for i in range(1, m+1):
for j in range(1, n+1):
dp[i][j] = grid[i-1][j-1] + min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])
return dp[-1][-1]
in-place 版:
class Solution:
def minPathSum(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
for i in range(1, m):
grid[i][0] += grid[i-1][0]
for j in range(1, n):
grid[0][j] += grid[0][j-1]
for i in range(1, m):
for j in range(1, n):
grid[i][j] += min(grid[i-1][j], grid[i][j-1])
return grid[-1][-1]
Review
What is semantic HTML and why is it important?
一个稍小众的关注点,为什么 HTML 要设计语义化,而且为什么它是重要的。
看完后忍不住用 Safari 的 Reader View 检验了下我的博客,并且会在未来调整布局时思考该文章的观点。
Tip
Python 里没有 ?: 这样的三元运算符,作为替代,a if condition else b 是最常见的写法,而文中提到的 Direct Method 也是很容易理解却不容易想到的方法,以 CheckiO 上的 Time Converter 题解举例:
def time_converter(time):
hour, minute = time.split(":")
hour = int(hour)
return f"{(hour - 1) % 12 + 1}:{minute} {'ap'[hour > 11]}.m."
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("Example:")
print(time_converter('12:30'))
#These "asserts" using only for self-checking and not necessary for auto-testing
assert time_converter('12:30') == '12:30 p.m.'
assert time_converter('09:00') == '9:00 a.m.'
assert time_converter('23:15') == '11:15 p.m.'
print("Coding complete? Click 'Check' to earn cool rewards!")
'ap'[hour > 11] 无疑是最简洁的方式,其实就是利用了 True、False 隐式转换为 1、0 而已。
Share
分享几个关于 Clean Code 的观点。
首先是为什么 Clean Code 很重要呢,我们列举下它的优点:
- 提高可维护性
- 让业务可持续发展
- 让你看起来更专业
- 易读、易理解
- 提高生产力
- 避免反复重新设计
- 让人愉悦
如何实现 Clean Code,或者说它的评估标准有哪些,这里展示一张网络上的图,通过它很容易判断项目当下 Clean Code 的级别以及需要思考改进的方向:

以此图为例,如果要深挖 *readability* 的定义,或许下面3条就是最完美的表达:
- 清晰 - “if you want to go fast, if you want to get done quickly, if you want your code to be easy to write, make it easy to read” — *Robert C. Martin*
- 简单 - 不要过度设计。
- 简洁 - 用最少的资源和最小的交互获得最大结果的艺术。
Clean Code 概念很大,可以延伸很广,未来有机会会做更多的分享。
